What is the circle of fifths and how is it used?
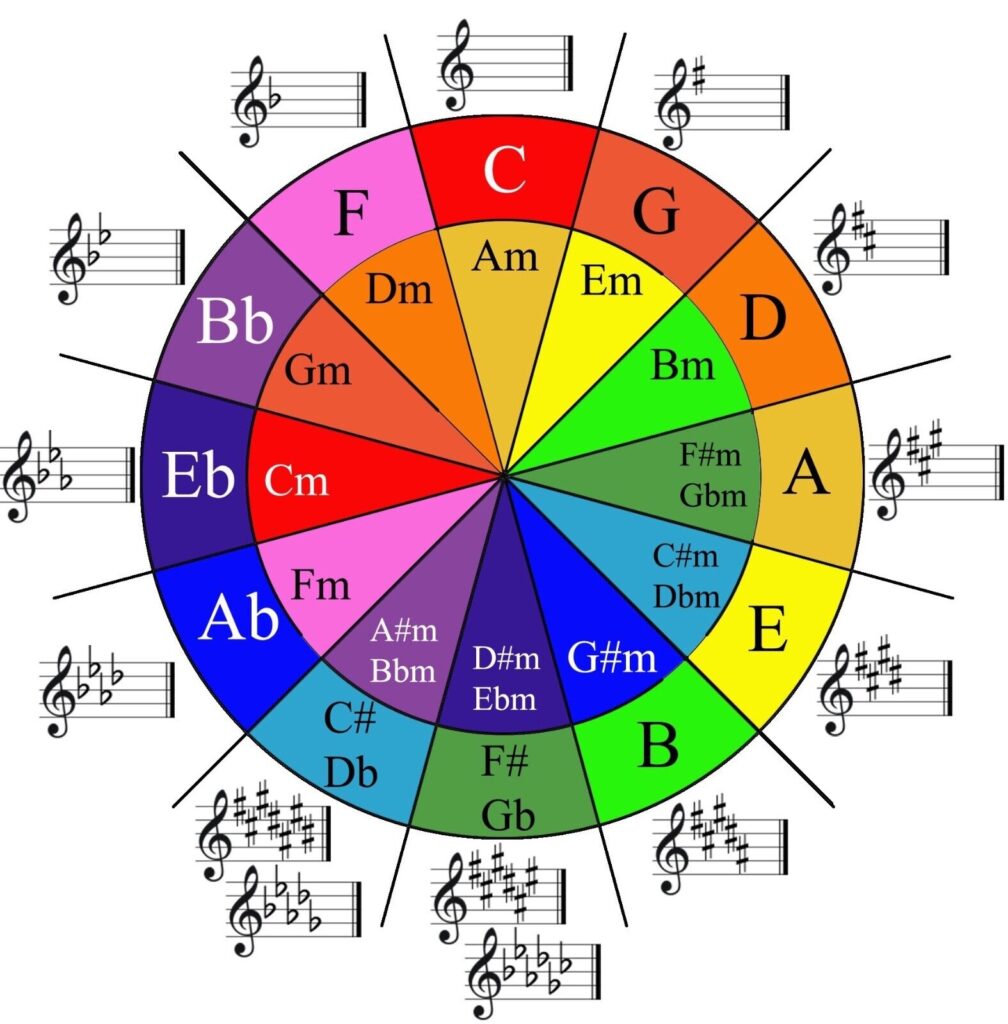
El círculo de quintas es una de las herramientas más útiles para cualquier músico, independientemente de su nivel de habilidad o experiencia. Es un concepto esencial en la teoría de la música que ayuda a los músicos a entender las relaciones entre las diferentes tonalidades y escalas. En su forma más básica, el círculo de quintas se utiliza para identificar las tonalidades relativas de una escala, pero también se puede utilizar para entender la progresión de acordes, las modulaciones de llave y mucho más.
El círculo de quintas es un diagrama que representa las relaciones entre las doce tonalidades de la escala cromática. En este círculo, cada tono está separado del siguiente por un intervalo de una quinta. La quinta es uno de los intervalos más fundamentales en la música y esto hace que el círculo de quintas sea una herramienta extremadamente útil para entender las conexiones entre las diferentes tonalidades.
El círculo de quintas se puede visualizar como un reloj, con las doce tonalidades dispuestas en un círculo. Comenzando en la parte superior del círculo con la tonalidad de C mayor (que no tiene sostenidos ni bemoles), cada tonalidad se mueve hacia la derecha en intervalos de una quinta. Por ejemplo, si empiezas en C y vas hacia la derecha, llegarás a G, que es una quinta por encima de C. Si sigues yendo hacia la derecha, llegarás a D, que es una quinta por encima de G, y así sucesivamente.
El círculo de quintas se utiliza de varias maneras en la teoría de la música. Uno de sus usos más comunes es ayudar a los músicos a entender las tonalidades relativas. Por ejemplo, si estás tocando una pieza en la tonalidad de C mayor y quieres saber cuál es la tonalidad relativa menor, simplemente puedes mirar el círculo de quintas. La tonalidad relativa menor siempre estará a la izquierda de la tonalidad mayor en el círculo de quintas, por lo que en este caso, la tonalidad relativa menor de C mayor sería A menor.
Otro uso común del círculo de quintas es entender las progresiones de acordes. En la música, es muy común que los acordes se muevan en intervalos de quintas. Por ejemplo, en una progresión de acordes I-IV-V (uno-cuatro-cinco), los acordes se mueven en intervalos de quintas. Si estás en la tonalidad de C mayor, los acordes serían C mayor (I), F mayor (IV) y G mayor (V). Si miras el círculo de quintas, verás que estos acordes están colocados uno al lado del otro.
El círculo de quintas también se puede usar para entender las modulaciones de llave. Una modulación es un cambio de tonalidad en una pieza de música. Si estás tocando en la tonalidad de C mayor y la música cambia a la tonalidad de G mayor, eso sería una modulación. Al mirar el círculo de quintas, puedes ver que G mayor está a la derecha de C mayor, lo que indica que la música ha modulado a una quinta por encima.
The circle of fifths is one of the most useful tools for any musician, regardless of their skill level or experience. It is an essential concept in music theory that helps musicians understand the relationships between different keys and scales. In its most basic form, the circle of fifths is used to identify the relative keys of a scale, but it can also be used to understand chord progressions, key modulations, and much more.
The circle of fifths is a diagram that represents the relationships between the twelve shades of the chromatic scale. In this circle, each tone is separated from the next by an interval of one fifth. The fifth is one of the most fundamental intervals in music and this makes the circle of fifths an extremely useful tool for understanding the connections between different keys.
The circle of fifths can be visualized as a clock, with the twelve keys arranged in a circle. Starting at the top of the circle with the key of C major (which has no sharps or flats), each key moves to the right in intervals of a fifth. For example, if you start at C and go to the right, you will reach G, which is one fifth above C. If you continue going to the right, you will reach D, which is one fifth above G, and so on.
The circle of fifths is used in various ways in music theory. One of its most common uses is to help musicians understand relative tonalities. For example, if you are playing a piece in the key of C major and want to know what the relative minor key is, you can simply look at the circle of fifths. The relative minor key will always be to the left of the major key on the circle of fifths, so in this case, the relative minor key of C major would be A minor.
Another common use of the circle of fifths is to understand chord progressions. In music, it is very common for chords to move in intervals of fifths. For example, in an I-IV-V (one-four-five) chord progression, the chords move in intervals of fifths. If you are in the key of C major, the chords would be C major (I), F major (IV), and G major (V). If you look at the circle of fifths, you will see that these chords are placed next to each other.
The circle of fifths can also be used to understand key modulations. A modulation is a change of key in a piece of music. If you are playing in the key of C major and the music changes to the key of G major, that would be a modulation. Looking at the circle of fifths, you can see that G major is to the right of C major, indicating that the music has modulated to a fifth above.
(https://academiasoldeando.com)